Network Motif Centrality
Definition
Based on network motifs and principal component analysis (PCA), Network Motif Centrality measure
node importance in directed biological networks.
For a network with n nodes, the procedures of the proposed measure are as follows:
Endow each motif with a weight wj, j= 1, 2,…,m, where wj=cj/Σmk=1ck here, ck(k = 1, 2,…,m) denotes the number of the k-th type of motif.
Matrix B computed as B=(bij)n×m = (b1,b2,...,bm) = (wjuij)n×m and Σ as covariance matrix of B.
Based on B and the idea of the PCA, the following index defined to obtain node importance score: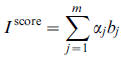 where α is eigenvector corresponding matrix Σ.
where α is eigenvector corresponding matrix Σ.
For a network with n nodes, the procedures of the proposed measure are as follows:
- Detect 2, 3 and 4-node network motifs in the network.
- Count the occurrences of each node in m types of motifs, and derive a n×m matrix A.
- Perform data processing on A, such as weighting and standardizing matrix A, then we obtain a matrix B. Compute the covariance matrix Σ of B.
- For Σ, compute the biggest eigenvalue λ and the corresponding unit eigenvector α.
- Compute Iscore and rank the n nodes accordingly.
Endow each motif with a weight wj, j= 1, 2,…,m, where wj=cj/Σmk=1ck here, ck(k = 1, 2,…,m) denotes the number of the k-th type of motif.
Matrix B computed as B=(bij)n×m = (b1,b2,...,bm) = (wjuij)n×m and Σ as covariance matrix of B.
Based on B and the idea of the PCA, the following index defined to obtain node importance score:
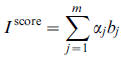
Software
References
- WANG, P., LÜ, J. & YU, X. 2014. Identification of Important Nodes in Directed Biological Networks: A Network Motif Approach. PLoS ONE, 9, e106132.
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106132


- WANG, P., YU, X. & LU, J. 2014. Identification and Evolution of Structurally Dominant Nodes in Protein-Protein Interaction Networks. Biomedical Circuits and Systems, IEEE Transactions on, 8, 87-97.