LAC - Local Average Connectivity-Based Method
Definition
Let Nv be the set of neighbors of node v. The subgraph G[Nv]
induced by Nv is named Cv. For a node w in Cv, distinguished from
its degree deg(ω) in G, its local connectivity in Cv is represented
as degCv (w). It is obvious that each node i in G has only one deg(i),
but has different degCv (i) with respect to different Cv. For each node
w∈Nv, its local connectivity degCv (w) is defined as how many other
nodes in Cv it connects directly. Then, the local average connectivity
of a node v (LAC(v)) is defined as the average local connectivity of
its neighbors:
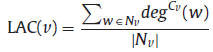 LAC(v) of a node v describes how close its neighbors are. Essentiality is, in many cases, a product
of complex function rather than an individual protein function.
The local average connectivity is such a local metric to determine
a protein’s essentiality based on the modular nature of protein
essentiality.
LAC(v) of a node v describes how close its neighbors are. Essentiality is, in many cases, a product
of complex function rather than an individual protein function.
The local average connectivity is such a local metric to determine
a protein’s essentiality based on the modular nature of protein
essentiality.
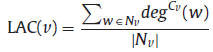
References
- LI, M., WANG, J., CHEN, X., WANG, H. & PAN, Y. 2011. A local average connectivity-based method for identifying essential proteins from the network level. Computational biology and chemistry, 35, 143-150.
DOI: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2011.04.002

