Current-Flow Closeness Centrality
Definition
The closeness index based on shortest paths can also be transformed to a measure based on electrical current. For the electrical current model set forth in [BRANDES, U. 2005], Brandes et al. developed an alternative measure of the distance between two vertices s and t, which is defined as the difference of their electrical potentials. Current-flow closeness centrality is defined by
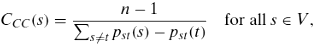 where (n−1) is a normalizing factor, pst(s) is the absolute electrical potential of vertex s based on the electrical current supply from vertex s to vertex t, and pst(s) − pst(t) corresponds to the effective resistance typically measured as voltage, which can be interpreted as an alternative measure of distance between s and t.
where (n−1) is a normalizing factor, pst(s) is the absolute electrical potential of vertex s based on the electrical current supply from vertex s to vertex t, and pst(s) − pst(t) corresponds to the effective resistance typically measured as voltage, which can be interpreted as an alternative measure of distance between s and t.
Brandes and Fleischer showed that current-flow closeness centrality is equivalent to information centrality [BRANDES, U. 2005].
See Information Centrality
Current flow group closeness centrality
Li, H., Peng, R., Shan, L., Yi, Y. and Zhang, Z., 2019, May. Current flow group closeness centrality for complex networks?. In The World Wide Web Conference (pp. 961-971).
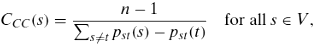
Brandes and Fleischer showed that current-flow closeness centrality is equivalent to information centrality [BRANDES, U. 2005].
See Information Centrality
Current flow group closeness centrality
Li, H., Peng, R., Shan, L., Yi, Y. and Zhang, Z., 2019, May. Current flow group closeness centrality for complex networks?. In The World Wide Web Conference (pp. 961-971).
Requirements
Require undirected, connected and loop free network.
Software
References
- BRANDES, U. & FLEISCHER, D. 2005. Centrality measures based on current flow, Springer.