Closeness Centrality
Definition
Freeman closeness centrality
Reciprocal of the total distance from a node v to all the other nodes in a network: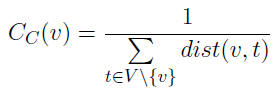 where dist(v, t) is the distance between node v and t.
where dist(v, t) is the distance between node v and t.
Typically it is used as a measure of how fast information will spread from one node in a network to all other nodes, or, in a network planning situation which nodes are favorable starting points.
Variant closeness centrality
By definition of shortest-path distances, classic closeness centrality is ill-defined on unconnected networks.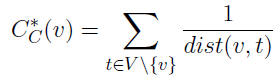 This variant (sum of inversed distances to all other nodes instead of the inversed of the sum of distances to all other nodes) [OPSAHL, T. 2010] applicable to both connected and unconnected graphs.
This variant (sum of inversed distances to all other nodes instead of the inversed of the sum of distances to all other nodes) [OPSAHL, T. 2010] applicable to both connected and unconnected graphs.
See Harmonic Centrality
Latora closeness centrality
In networks with disconnected components
Latora V., Marchiori M., Efficient behavior of small-world networks, Physical Review Letters, V. 87, p. 19, 2001.
Fuzzy closeness centrality
A closeness centrality measure, with a fuzzy distance measure in the graph.
DAVIDSEN, S. A. & PADMAVATHAMMA, M. A fuzzy closeness centrality using andness-direction to control degree of closeness. Networks & Soft Computing (ICNSC), 2014 First International Conference on, 19-20 Aug. 2014 2014. 203-208.
See Fuzzy Closeness Centrality
Dangalchev closeness centrality
DANGALCHEV, C. 2006. Residual closeness in networks. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 365, 556-564. DOI: 10.1016/j.physa.2005.12.020.
See Dangalchev Closeness Centrality
Residual closeness centrality
DANGALCHEV, C. 2006. Residual closeness in networks. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 365, 556-564. DOI: 10.1016/j.physa.2005.12.020.
See Residual Closeness Centrality
Closeness centrality for a set of nodes
Chen, C., Wang, W. and Wang, X., 2016, September. Efficient Maximum Closeness Centrality Group Identification. In Australasian Database Conference (pp. 43-55). Springer International Publishing. See Closeness Centrality Group Identification
Top-k closeness centrality on dynamic networks
Lin, Y., Zhang, J., Ying, Y., Hong, S. and Li, H., 2016, September. FVBM: A Filter-Verification-Based Method for Finding Top-k Closeness Centrality on Dynamic Social Networks. In Asia-Pacific Web Conference (pp. 389-392). Springer International Publishing.
Edge Closeness centrality
Bröhl, T. and Lehnertz, K., 2019. Centrality-based identification of important edges in complex networks. Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, 29(3), p.033115.
Ni, P., Hanai, M., Tan, W.J. and Cai, W., 2019, August. Efficient closeness centrality computation in time-evolving graphs. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining (pp. 378-385).
Shukla, K., Regunta, S.C., Tondomker, S.H. and Kothapalli, K., 2020, June. Efficient parallel algorithms for betweenness-and closeness-centrality in dynamic graphs. In Proceedings of the 34th ACM International Conference on Supercomputing (pp. 1-12).
Reciprocal of the total distance from a node v to all the other nodes in a network:
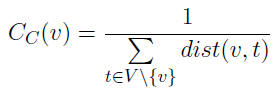
Typically it is used as a measure of how fast information will spread from one node in a network to all other nodes, or, in a network planning situation which nodes are favorable starting points.
Variant closeness centrality
By definition of shortest-path distances, classic closeness centrality is ill-defined on unconnected networks.
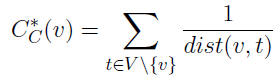
See Harmonic Centrality
Latora closeness centrality
In networks with disconnected components
Latora V., Marchiori M., Efficient behavior of small-world networks, Physical Review Letters, V. 87, p. 19, 2001.
Fuzzy closeness centrality
A closeness centrality measure, with a fuzzy distance measure in the graph.
DAVIDSEN, S. A. & PADMAVATHAMMA, M. A fuzzy closeness centrality using andness-direction to control degree of closeness. Networks & Soft Computing (ICNSC), 2014 First International Conference on, 19-20 Aug. 2014 2014. 203-208.
See Fuzzy Closeness Centrality
Dangalchev closeness centrality
DANGALCHEV, C. 2006. Residual closeness in networks. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 365, 556-564. DOI: 10.1016/j.physa.2005.12.020.
See Dangalchev Closeness Centrality
Residual closeness centrality
DANGALCHEV, C. 2006. Residual closeness in networks. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 365, 556-564. DOI: 10.1016/j.physa.2005.12.020.
See Residual Closeness Centrality
Closeness centrality for a set of nodes
Chen, C., Wang, W. and Wang, X., 2016, September. Efficient Maximum Closeness Centrality Group Identification. In Australasian Database Conference (pp. 43-55). Springer International Publishing. See Closeness Centrality Group Identification
Top-k closeness centrality on dynamic networks
Lin, Y., Zhang, J., Ying, Y., Hong, S. and Li, H., 2016, September. FVBM: A Filter-Verification-Based Method for Finding Top-k Closeness Centrality on Dynamic Social Networks. In Asia-Pacific Web Conference (pp. 389-392). Springer International Publishing.
Edge Closeness centrality
Bröhl, T. and Lehnertz, K., 2019. Centrality-based identification of important edges in complex networks. Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, 29(3), p.033115.
Ni, P., Hanai, M., Tan, W.J. and Cai, W., 2019, August. Efficient closeness centrality computation in time-evolving graphs. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining (pp. 378-385).
Shukla, K., Regunta, S.C., Tondomker, S.H. and Kothapalli, K., 2020, June. Efficient parallel algorithms for betweenness-and closeness-centrality in dynamic graphs. In Proceedings of the 34th ACM International Conference on Supercomputing (pp. 1-12).
Requirements
Require connected and strongly connected network.
Software
- AllegroGraph
http://franz.com/agraph/allegrograph/ - CentiBiN
http://centibin.ipk-gatersleben.de/ - CentiLib
http://centilib.ipk-gatersleben.de/ - CentiScaPe
http://www.cbmc.it/~scardonig/centiscape/centiscape.php - CytoNCA
http://apps.cytoscape.org/apps/cytonca - EgoNet
http://escoladeredes.net/profiles/blogs/egonet-1 - GraphStream
http://graphstream-project.org/ - graph-tool
http://graph-tool.skewed.de/ - igraph
http://igraph.org - Interference
http://www.cbmc.it/~scardonig/interference/Interference.php - JGraphT-sna
https://bitbucket.org/sorend/jgrapht-sna - JUNG
http://jung.sourceforge.net - MultiNet
http://www.sfu.ca/personal/archives/richards/Multinet/Pages/multinet.htm - neo4j
http://neo4j.com/ - NetVis Module
http://www.netvis.org/ Module
- NetworkAnalyzer
http://med.bioinf.mpi-inf.mpg.de/networkanalyzer/ - NetworkX
https://networkx.github.io/ - NodeXL
http://nodexl.codeplex.com/ - Pajek
http://pajek.imfm.si/ - qgraph
http://sachaepskamp.com/qgraph - RINalyzer
http://rinalyzer.de/ - RINspector
http://apps.cytoscape.org/apps/rinspector - SBEToolbox
https://github.com/biocoder/SBEToolbox/releases - Sentinel Visualizer
http://www.fmsasg.com/SocialNetworkAnalysis/ - sna
http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=sna - SocNetV
http://socnetv.sourceforge.net/ - tnet
http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/tnet/ - UCINET
https://sites.google.com/site/ucinetsoftware/ - Visone
http://visone.info/ - WebGraph
http://webgraph.di.unimi.it/ - Wolfram
http://www.wolfram.com
References
- FREEMAN, L. C. 1978. Centrality in social networks conceptual clarification. Social Networks, 1, 215-239.
DOI: 10.1016/0378-8733(78)90021-7


- OPSAHL, T., AGNEESSENS, F. & SKVORETZ, J. 2010. Node centrality in weighted networks: Generalizing degree and shortest paths. Social Networks, 32, 245-251.
DOI: 10.1016/j.socnet.2010.03.006


- Chen, C., Wang, W. and Wang, X., 2016, September. Efficient Maximum Closeness Centrality Group Identification. In Australasian Database Conference (pp. 43-55). Springer International Publishing.
- Lin, Y., Zhang, J., Ying, Y., Hong, S. and Li, H., 2016, September. FVBM: A Filter-Verification-Based Method for Finding Top-k Closeness Centrality on Dynamic Social Networks. In Asia-Pacific Web Conference (pp. 389-392). Springer International Publishing.
- Saxena, A., Gera, R. and Iyengar, S.R.S., Fast Estimation of Closeness Centrality Ranking.