Bipartivity
Definition
The contribution of node i to network bipartivity, β (i), can be obtained by using the
subgraph centrality of node i:
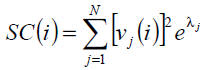 where (v1, v2, ..., vn) is an orthonormal basis of RN composed by eigenvectors of the adjacency
matrix associated with the eigenvalues λ1, λ2, ..., λn, and vj(i) is the ith component of vj. Hence,
β(i) is given by:
where (v1, v2, ..., vn) is an orthonormal basis of RN composed by eigenvectors of the adjacency
matrix associated with the eigenvalues λ1, λ2, ..., λn, and vj(i) is the ith component of vj. Hence,
β(i) is given by:
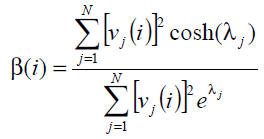
Note: The values of β are confined to the interval [0.5, 1]. According to [ESTRADA, E. 2006], lethal proteins tend to have a low bipartivity score. Therefore you must adjust the value by setting it to 1 − β(i), such that lethal proteins potentially have a higher score.
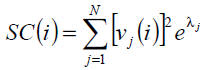
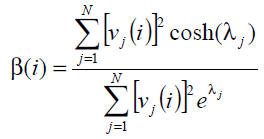
Note: The values of β are confined to the interval [0.5, 1]. According to [ESTRADA, E. 2006], lethal proteins tend to have a low bipartivity score. Therefore you must adjust the value by setting it to 1 − β(i), such that lethal proteins potentially have a higher score.
Software
References
- ESTRADA, E. & RODRÍGUEZ-VELÁZQUEZ, J. A. 2005. Spectral measures of bipartivity in complex networks. Physical Review E, 72, 046105.
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.72.046105


- ESTRADA, E. 2006. Protein Bipartivity and Essentiality in the Yeast Protein−Protein Interaction Network. Journal of Proteome Research, 5, 2177-2184.
DOI: 10.1021/pr060106e

